✔SCYTALE CIPHER
Type: Transposition
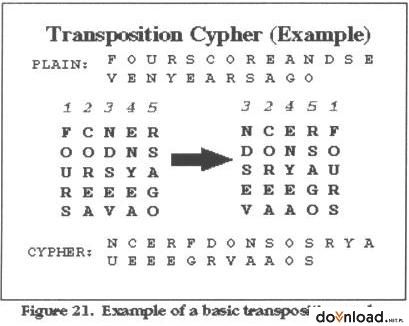
> Suppose the rod allows one to write four letters around in a circle and five letters down the side of it. To decrypt, all one must do is wrap the leather strip around the rod and read across.
(Note: make a table and insert there your input, table is based on diameter)
Example message:
Plaintext: Hey i was doing just fine before i met you
Diameter: 7
H|E|Y| I|W|A|S
D|O| I|N|G|J|U
S|T|F| I|N|E|B
E|F|O|R|E| I|M
E|T|Y|O|U|
Ciphertext: HDSEEEOTFTYIFOY
INIROWGNEUAJEISUBM
✔ROTATION CODE
Type: Substitution
(Note: it’s formula forencryption is f(x)=(ax)mod26 and for decryption is f(y)=a^-1(y)mod
26, where x or y corresponds to the position of the letter in the alphabet, e.g. a=0, b=1, c=2…..z=25, mod26 correspond to the limit of the rotation, and a correspond to any input number)
Example: (encryption)
Plaintext: KING
F(x)=(ax)mod26
a=2
K=10, f(x)=(2*10)mod26=20
I =8, f(x)=(2*8)mod26=16=
N=13, f(x)=(2*13)mod26=26
G=6, f(x)=(2*6)mod26=12
K=20=U
I =16=Q
N=26=A
G=12=M
Ciphertext: UQAM
Example: (decryption)
Ciphertext: UQAM
F(y)=a^-1(y)mod26
a=2
U=20, f(y)=2^-1(20)mod26=10
Q=16, f(y)=2^-1(16)mod26=8
A=26, f(y)=2^-1(26)mod26=13
M=12, f(y)=2^-1(12)mod26=6
U=10=K
Q=8=I
A=13=N
M=6=G
Plaintext: KING
(Note: mod26, when no>25, then it will rotate back to 0, 26=0, 27=1, 28=2 and so on, where a=0 and z=25, e.g. 30=e)
✔AFFINE CIPHER
Type: Substitution
(Note: it’s formula for encryption is f(x)=(ax+b)mod n, and for decryption is f(y)=a^-1(y-b)m
od n, where “a” should be coprime of “n”, “x” or “y” corresponds on the position of the letter in the alphabet (see rotation code), and “b” is any value of input, and mod n is the limit of rotation)
Example: (encryption)
Plaintext: AFFINE
a=5, b=8, n=26
F(x)=(ax+b)mod26
A=0, F(0)=(5(0)+8)mod26=8
F=5, F(5)=(5(5)+8)mod26=33
F=5, F(5)=(5(5)+8)mod26=33
I =8, F(8)=(5(8)+8)mod26=48
N=13, F(13)=(5(13)+8)mod26=73
E=4, F(4)=(5(4)+8)mod26=28
A=08=I
F=33=H
F=33=H
I =48=W
N=73=V
E=28=C
Ciphertext: IHHWVC
Example: (decryption)
Ciphertext: IHHWVC
a=5, b=8, n=26
F(y)=a^-1(y-b)mod n
I =08, f(8)=5^-1(8-8)mod26=0
H=33, f(33)=5^-1(33-8)mod26=5
H=33, f(33)=5^-1(33-8)mod26=5
W=48, f(48)=5^-1(48-8)mod26=8
V=73, f(73)=5^-1(73-8)mod26=13
C=28, f(28)=5^-1(28-8)mod26=4
I =0=A
H=5=F
H=5=F
W=8=I
V=13=N
C=5=E
Plaintext: AFFINE
✔RAIL FENCE CIPHER
Type: Transposition
(Note: shift depends on no. key or rails, and letters should be written downward and diagonally, let `=no. of shift or rails)
Plaintext: HEY I JUST MET YOU AND THIS IS CRAZY
shift: 3
h ` ` ` j ` ` ` m ` ` ` o ` ` ` d ` ` ` s ` ` ` r ` ` `
` e ` i ` u ` t ` e ` y ` u ` n ` t ` i ` i ` c ` a ` y
` ` y ` ` ` s ` ` ` t ` ` ` a ` ` ` h ` ` ` s ` ` ` z `
Ciphertext:
HJMODSREIUTEYUNTIICAYYSTAHSZ
✔POLYBIUS SQUARE
Type: Numbers
> Polybius square, also known as the Polybius checkerboard, is a device invented by the Ancient Greekhistorian and scholar Polybius, for fractionating plaintext characters so that they can be represented by a smaller set of symbols.
(Note: create a table of any size, readings should start in column then row)
Example:5×5
 A B C D E
A|A|B|C|D|E
B|F|G|H|J|K
C|L|M|N|O|P
D|Q|R|S|T|U
E|V|W|X|Y|Z
Ciphertext: CB CD CC BD AA ED
Plaintext: M O N D A Y
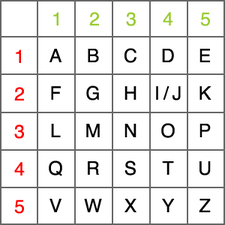
✔VIGENERE CIPHER
Type: Substitution
(Note: keywords sets at the starting point of alphabet and keyword shoud be inserted in the first column of the table mot in the row, keyword shoud be repeated until it reach the same value or no. of the text )
Example:
Plaintext: JUPITER
Keyword: mapsmap
(See vigenere table)
Ciphertext: VUEAFEG
✔HITMAN CIPHER
If A is A then N is N.
A~A
B~Z
C~Y
D~X
E~W
F~V
G~U
H~T
I~S
J~R
K~Q
L~P
M~O
N~N
Example
Ciphertext: TSHOAN
Plaintext: HITMAN
✔BIFID CIPHER
Type: Substitution
CIPHER: First column and firs row contains numbers while the rest is letters) 5×5
Example:
1 2 3 4 5
1|A|B|C|D|E|
2|F|G|H| I |K|
3|L|M|N|O|P|
4|Q|R|S|T|U|
5|V|W|X|Y|Z|
Ciphertext: 3,2 3,4 3,3 4,3 4,4 1,5 4,2 or
Ciphertext: 32 34 33 43 44 15 42
Plaintext: MONSTER
✔TAP CODE
type: Substitution
A(. .)
B(. ..)
C(. …)
D(. ….)
E (. …..)
F (.. .)
G(.. ..)
H(.. …)
I(.. ….)
J(.. …..)
K(. …)
L(… .)
M(… ..)
N(… …)
O(… ….)
P(… …..)
Q(…. .)
R(…. ..)
S(…. …)
T(…. ….)
U(…. …..)
V(….. .)
W(….. ..)
X(….. …)
Y(….. ….)
Z(….. …..)
*space* (null)
DOT DOT CODES
A(°••••)
B(•°•••)
C(••°••)
D(•••°•)
E(••••°)
F(•°°°°)
G(°•°°°)
H(°°•°°)
I(°°°•°)
J(°°°°•)
K(°•°•°)
L(•°•°•)
M(••°°°°)
N(°°••°°)
O(°°°°••)
P(°°••••)
Q(••°°••)
R(••••°°)
S(•°•°°)
T(°•°°•)
U(•°°•°)
V(°°•°•)
W(°•°••)
X(•°••°)
Y(°••°•)
Z(••°•°)
✔NEWS CIPHER
(Note: make a table of letters, whether theres a keyword or none, 5×5 from A to Z, where C/K and I/J are interchangeable.)
Legends:
N ~ North
E ~ East
W ~ West
S ~ South
NE ~ North East
NW ~ North West
SE ~ South East
SW ~ South West
A | B | C | D | E
F | G | H | I | J
L | M| N | O | P
Q | R | S | T | U
V | W| X | Y | Z
Example:
Ciphertext: NWFNVNEDSBWISWFN
N(W) F(N) V(NE) D(S) B(W) I(SW) F(N)
Plaintext: MARIANA
✔CROSS CODE
A ~ †††
B ~ +††
C ~ †+†
D ~ ††+
E ~ †++
F ~ +†+
G ~ ++†
H ~ ࠠ
I ~ †‡†
J ~ ††‡
K ~ ‡++
L ~ +‡+
M ~ ++‡
N ~ †‡‡
O ~ ‡†‡
P ~ ‡‡†
Q ~ +‡‡
R ~ ‡+‡
S ~ ‡‡+
T ~ ‡†+
U ~ †+‡
V ~ +‡†
W ~ ‡+†
X ~ +†‡
Y ~ †‡+
Z ~ +++
✔ARROW CODES
(Note: Create a table of letters 5×5 either theres a keyword or none, and moves starts after the first given letter)
Legends: ←↑↓→
Moves: ¹ ² ³ ⁴
/-separates each letters
A | B | C | D | E
F | G | H | I | J
L | M| N | O | P
Q | R | S | T | U
V | W| X | Y | Z
Example:
Codex: P/ ←⁴↑²/ →²↓²/ →¹↑²/ ↓²/ ←²↓¹/ ←¹↑³/
Plaintext: PANDORA
*note: follow the arrow
—Nihilist Cipher—
//This cipher was developed and used by Russian nihilists to communicate with allies during a particular war.//
First, is kelangan mo munang gumawa ng polybius square.
°| 1 2 3 4 5
———————–
1| A B C D E
2| F G H I J
3| K L M N O
4| P R S T U
5| V W X Y Z
Then, pumili ka ng secret word. Ang example ko is MIX.. Then I write out mo ito ng paulit ulit sa message mo sa baba into. For example ang message naten is GIVE IT TO ME.
GIVEITTOME
MIXMIXMIXM
Then base sa polybius square, i coconvert mo sila into numbers.
22 24 51 15 24 44 44 35 33 15
33 24 53 33 24 53 33 24 53 33
And lastly, para maencrypt is iaadd mo lang sila.
Final encrypted message is…
55 48 104 48 48 97 77 59 86 48
Gets?
Decode this using the secret word FISH.
73 35 75 34 55 46 64 58 63 39 94 38 63
—CLOCK CIPHER—
From France Bayongasan
Sa gustong matuto ng clock cipher ito na po
Clock cipher
Am=A
1=B
2=C
3=D
4=E
5=F
6=G
7=H
8=I
9=J
10=K
11=L
12=M
13=N
14=O
15=P
16=Q
17=R
18=S
19=T
20=U
21=V
22=W
23=X
24=Y
Pm=Z
00=SPACE
—From Markjoseph Kish—
Para mas lalo nyong maintindihan ang Binary Clock kailangan gumawa ng table(4 pababa,2 pahalang pero tatlong chart) parang ganito
8 °° | °° | °°
4 °° | °° | °°
2 °° | °° | °°
1 °° | °° | °°
Ganyan ang gagawin
°(di nailaw)
•(nailaw)
Kung ano lang yung nailaw ayun lang ang bibilangin nyo…
Tulad nito
°°|°°|°°
°°|°°|°°
°•|•°|°°
°•|•°|°°
=03:30:00
Kapag double ang ilaw sa isang line ay iaadd nyo lang
Credits to my Bos (JB)